Chemistry 1 Formula Writting and Naming Continued Practice Extra Practice for Quiz 1
Doing practice problems is the only way to master organic chemistry! At Chemistry Steps, you can find all the topics of Organic 1 and 2 and their associatedpractice problems. There are more than 1000 practice questions and you can find them after each article listed below.
Here are some examples from the topics shown below.
Note : These are sample practice problems for the new users. Please go to the topics and where you can practice problems after the articles or in a separate post.
Registered members can access all the quizzes and their solutions too.
Organic Chemistry 1 Practice Problems
Structure and Bonding Practice Problems
Convert the following condensed structures into Bond-line structures:
a) CH3CONHCH2OCH3
b) O(CH2)3CHCH3
c) CH3CHCHN(CH3)CH2CH3
d) (CH3)3CCH2CH2COOCH2CH3
e) CH3CH2CCCH2CO(CH2)2N(CH3)2
f) CH3CH2C(CH3)CHCH(CH2)4
g) (CH3)2CCHCH2OCH(CH3)CH2CN
h) CH3CH2CHClCHBrCH2CONHCH(CH3)2
i) (CH3)2CHCCCH2OCH(CH2Br)CH2CH3
j) CH3NHCHCCH3CHClCON(C2H5)2
Answers and Solutiuons
Molecular Representations
Practice Problems
Identify the delocalized lone pairs of electrons for each of the following compounds and draw at least one resonance structure using the delocalized lone pairs.

Answers and Solutions
Acids and Bases Practice Problems
Using the pKa table, determine a suitable reagent to deprotonate the following compounds.Each reagent can only be used once.Indicate the pKa values and write the second product as well.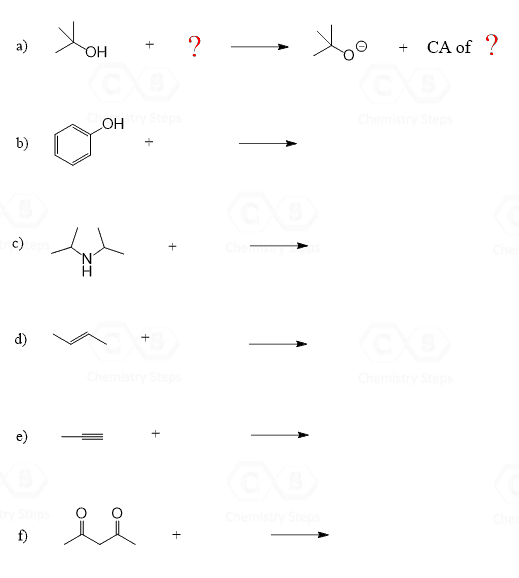
Answers and Solutions
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Practice Problems
Draw both chair conformation (ring-flip) and use the table to calculate the relative energy cost associated with each group in the axial position to determine the more stable chair conformation of each of the following compounds:

Answers and Solutions
Stereochemistry Practice Problems
Determine if each of the following alkenes has an E orZconfiguration:

Answers and Solutions
Determine the relationship in each of the following pairs. Do the drawings represent constitutional isomers or stereoisomers, or are they just different ways of drawing the same compound? If they are stereoisomers, are they enantiomers or diastereomers?
Explain your answer by converting the drawings into the same representation, i.e. if you are comparing a Newman projection to a Fischer projection, you need to convert both into either a Newman or Fischer projection. Assign all the absolute configurations asR orS if you hesitate.

Answers and Solutions
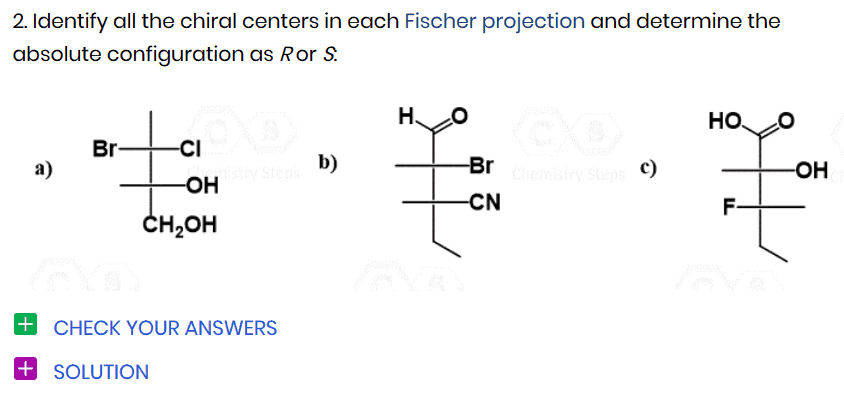
Identify all the chiral centers in each molecule and determine the absolute configuration asR orS:

Answers and Solutions
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions
Practice Problems
Predict the mechanism as SN1, SN2, E1 or E2 and draw the major organic product formed in each reaction. Consider any regioselectivity and stereoselectivity where applicable:

Answers and Solutions
Reactions of Alkenes Practice Problems
Identify the reagents for each of the following addition reaction to an alkene:

Predict the product(s) that are formed after each step for reactionsA-G. In each case, consider formation of any chiral center(s) and draw all expected stereoisomers.
This is a comprehensive problem that covers the following topics and will serve as a review of all of them:
Substitution and elimination reactions. Particularly, substitution and elimination reactions of alcohols, the regio– and stereochemistry of E2 reactions and E2 reaction of cyclohexanes.
Mesylation and tosylation in Substitution and elimination reactions.
Hydrohalogenation of alkenes according to the Markovnikov's rule.
Radical hydrohalogenation of alkenes.
Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkenes.
Halogenation of alkenes through halohydrin formation.
Syn and anti dihydroxilation of alkenes.
Elimination reactions: Zaitsev and Hoffman products.
Ozonoloysis of Alkenes.

Attempt solving the entire problem before accessing the answers!
Theanswers will give you the structure of thefinal product(s) only. Use this as a hint to determine the compounds formed after the first and second reactions.
Answers and Solutions
Reactions of Alkynes Practice Problems
Identify the reagents for each of the following reactions of internal and terminal alkynes:

On the following synthetic scheme, identify the reagents, in the correct order, that you would use to achieve the following synthetic transformations. Determine the structure of compounds A and B and the major organic products resulting from the alkyne.

Organic Chemistry 2 Practice Problems
NMR Spectroscopy Practice Problems
The1H NMR spectrum of compound X (C4H8O2 ) is shown below. It also shows a strong IR absorption band near 1730 cm−1. Propose a structure for X.

Answers and Solutions
IR Spectroscopy
Label the functional groups and identify the correct compound based on the IR spectrum.

Radicals Practice Problems
Predict the products when each of the following compounds is treated with NBS under UV light:

Answers and Solutions
Alcohols Practice Problems
Predict the major organic product(s) for the following Grignard reactions of a ketone, aldehyde, ester, carbon dioxide and an epoxide:

Answers and Solutions
Predict the major organic product when the following alcohol is treated with each oxidizing agent:

Answers and Solutions
The Diels-Alder Reaction Practice Problems
For each Diels–Alder reaction, predict the major product(s) with correct stereochemistry when each cyclic diene is reacted with a dienophile:

Aromatic Substitution Practice Problems
Show how each compound can be synthesized from benzene and any other organic or inorganic reagents.
The order of reactions is very important! So, before every step,consider the ortho– , para– , or meta directing effect of the current group on the aromatic ring.
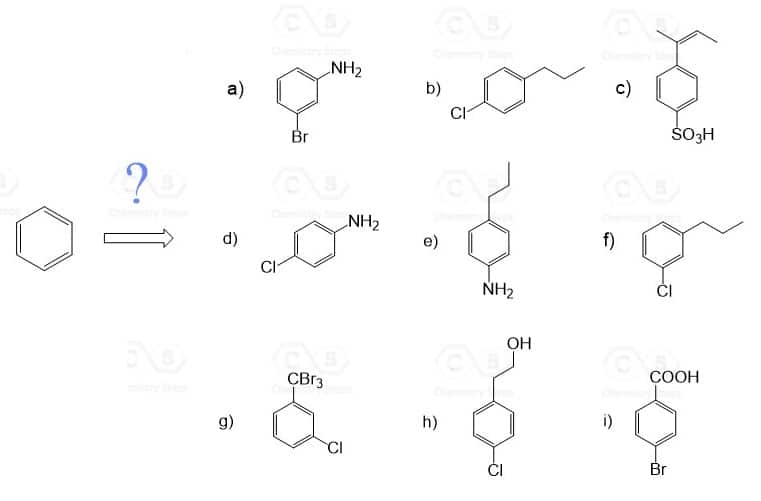
Devise a synthesis of each of the following compounds using an arene diazonium salt. They all require more than one step and you may select the desired regioisomer (for example the para product from an ortho, para mixture) when needed.

Answers and Solutions
Aldehydes and Ketones Practice Problems
Predict the major product(s) obtained when each of the following compounds undergoes hydrolysis in the presence of an acid:
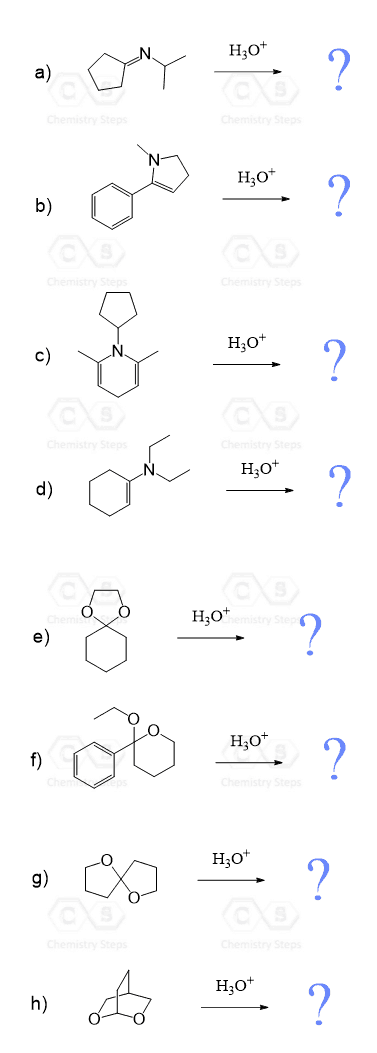
Answers and Solutions
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Practice Problems
Predict themajor organic product(s) for each of the following reactions. Theyall involve carboxylic acid derivatives such asesters, acid chlorides, nitriles, anhydrides, and amides. You may also need to go over the reactions covered in earlier chapters, particularly, theGrignard andGilman reagents,oxidizing andreducingagents andelectrophilic aromatic substitutions.
A link to each topic encountered in a given problem will be provided in the answer tab.

Answers and Solutions
Alpha Carbon Chemistry – Enols and Enolates Practice Problems
his is acomprehensive practice problem on the alpha carbon chemistry. The topics covered range from the simple halogenation reactions of enols tomultistep synthetic transformation.
To correctly answer these questions, you need to review the main principles of enolate chemistry – direct enolate alkylation, aldol condensation, crossed aldol condensation, alkylation using acetoacetic ester synthesis, malonic ester synthesis, the Stork enamine synthesis, Claisen condensation, Michael addition, and Robinson annulation.
Practice
Propose an efficient strategy to achieve each of the following synthetic transformations and show the structure of all the key intermediates.

Answers and Solutions
Check out our new synthesis puzzles!

CS Prime membership will also grant you access to multiple-choice quizzes!
Free

General Chemistry Overview Quiz
Free

Molecular Representations Quiz
Free

Organic Acids and Bases Quiz
Free

Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Practice Quiz
Free

Stereochemistry Practice Problems Quiz
Free

Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Practice Quiz
Free

Alkene Addition Reactions Practice Quiz
Free

Alkyne Naming and Reactions Practice Quiz
Free

Organic Chemistry Final Practice Quiz
Free

Aromatic Compounds
Free

Alcohols Quiz – Naming, Preparation, and Reactions
Free

Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Practice Quiz
Free

Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Quiz
Free

Carbohydrates Practice Problem Quiz
Free

IUPAC Nomenclature Summary Quiz
Table of Content
Structure and Bonding
- Lewis Structures in Organic Chemistry
- Valency and Formal Charges in Organic Chemistry
- sp3, sp2, and sp Hybridization in Organic Chemistry with Practice Problems
- How to Quickly Determine The sp3, sp2 and sp Hybridization
- Molecular and Electron Geometry of Organic Molecules with Practice Problems
Molecular Representations
- Bond-Line or Skeletal Structures
- Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry
- Converting between Bond-line, Lewis and Condensed Structures with Practice Problems
- Curved Arrows with Practice Problems
- Resonance Structures in Organic Chemistry
- How to Choose the More Stable Resonance Structure
- Drawing Complex Patterns in Resonance Structures
- Localized and Delocalized Lone Pairs with Practice Problems
Acids and Bases
- Organic Acids and Bases
- Organic acid-base mechanisms
- Acid Strength and pKa
- How to Determine the Position of Equilibrium for an Acid–Base Reaction
- Factors That Determine the pKa and Acid Strength
- How to Choose an Acid or a Base to Protonate or Deprotonate a Given Compound
- Lewis Acids and Bases
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
- Naming Alkanes by IUPAC nomenclature Rules Practice Problems
-
How to Name a Compound with Multiple Functional Groups
- Primary Secondary and Tertiary Carbon Atoms in Organic Chemistry
- Constitutional or Structural Isomers with Practice Problems
- Degrees of Unsaturation or Index of Hydrogen Deficiency
- Newman Projections with Practice Problems
- Gauche Conformation, Steric, Torsional Strain Energy Practice Problems
- Drawing the Chair Conformation of Cyclohexane
- Ring Flip: Drawing Both Chair Conformations with Practice Problems
- 1,3-Diaxial Interactions and A value for Cyclohexanes
- Ring-Flip: Comparing the Stability of Chair Conformations with Practice Problems
- Cis and Trans Decalin
Stereochemistry
- Enantiomers Diastereomers the Same or Constitutional Isomers with Practice Problems
- Chirality and Enantiomers: Determine if Enantiomers or Identical based on R and S Configuration
- Cis and Trans Stereoisomerism in Alkenes
- E and Z Alkene Configuration with Practice Problems
- How to Determine the R and S configuration
- The R and S Configuration Practice Problems
- Determine the Relationship – Enantiomers Diastereomers or Constitutional Isomers
- Optical Activity
- Enantiomeric Excess (ee): Percentage of Enantiomers from Specific Rotation with Practice Problems
- Calculating Enantiomeric Excess from Optical Activity
- Symmetry and Chirality. Meso Compounds
- Fischer Projections with Practice Problems
- Resolution of Enantiomers: Separate Enantiomers by Converting to Diastereomers
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 – How to Choose the Mechanism
- Is it SN1 SN2 E1 or E2 Mechanism With the Largest Collection of Practice Problems
- Introduction to Alkyl Halides
- Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
- Introduction to Substitution Reactions
- All You Need to Know About the SN2 Reaction Mechanism
- The SN2 Mechanism: Kinetcis, Thermodynamics, Curved Arrows and Stereochemistry with Practice Problems
- Mechanism and Stereochemistry of SN2 Reactions with Practice Problems
- Mesylates and Tosylates as Good Leaving Groups
- SOCl2 and PBr3 for Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides
- The SN1 Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction
- The SN1 Mechanism: Kinetcis, Thermodynamics, Curved Arrows and Stereochemistry with Practice Problems
- The Substrate and Nucleophile in SN2 and SN1 Reactions
- The Role of the Solvent in SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 Reactions
- Carbocation Rearrangements in SN1 Reactions with Practice Problems
- When Is the Mechanism SN1 or SN2?
- How to Choose Molecules for Doing SN2 and SN1 Synthesis-Practice Problems
- Alcohols in Substitution Reactions with Tons of Practice Problems
Alkenes: Structure, Stability and Nomenclature
- Naming Alkenes by IUPAC Nomenclature Rules
- Cis and Trans Stereoisomerism in Alkenes
- E and Z Alkene Configuration with Practice Problems
Elimination Reactions
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 – How to Choose the Mechanism
- Is it SN1 SN2 E1 or E2 Mechanism With the Largest Collection of Practice Problems
- General Features of Elimination
- The E2 Mechanism
- Zaitsev's Rule – Regioselectivity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- The Hofmann Elimination of Amines and Alkyl Fluorides
- Stereoselectivity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- Stereospecificity of E2 Elimination Reactions
- Elimination Reactions of Cyclohexanes with Practice Problems
- POCl3 for Dehydration of Alcohols
- The E1 Mechanism: Kinetcis, Thermodynamics, Curved Arrows and Stereochemistry with Practice Problems
- Dehydration of Alcohols by E1 and E2 Elimination
- Stereoselectivity of E1 Reactions
- Nucleophilic Substitution vs Elimination Reactions
- Regioselectivity of E1 Reactions
- E2 vs. E1 Elimination Mechanism with Practice Problems
Addition Reactions of Alkenes
- Markovnikov's Rule with Practice Problems
- The Stereochemistry of Alkene Addition Reactions
- Free-Radical Addition of HBr: Anti-Markovnikov Addition
- Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes with Practice Problems
- Oxymercuration-Demercuration
- Hydroboration-Oxidation: The Mechanism
- Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkenes: Regiochemistry and Stereochemistry with Practice Problems
- Halogenation of Alkenes and Halohydrin Formation
- Ozonolysis of Alkenes with Practice Problems
- Syn Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with KMnO4 and OsO4
- Anti Dihydroxylation of Alkenes with MCPBA and Other Peroxides with Practice Problems
- Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes with KMno4 and O3
- Cis product in an anti Addition Reaction of Alkenes
- Alkene Reactions Practice Problems
- Changing the Position of a Double Bond
- Changing the Position of a Leaving Group
- Alkenes Multi-Step Synthesis Practice Problems
- Addition of Alcohols to Alkenes
Alkynes
- Introduction to Alkynes
- Naming Alkynes by IUPAC Nomenclature Rules – Practice Problems
- Preparation of Alkynes by Elimination Reactions
- Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes
- Acid Catalyzed Hydration of Alkynes with Practice Problems
- Reduction of Alkynes
- Halogenation of Alkynes
- Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkynes with Practice Problems
- Ozonolysis of Alkynes with Practice Problems
- Alkylation of Terminal Alkynes in Organic Synthesis with Practice Problems
- Alkyne reactions summary practice problems
- Alkyne Synthesis Reactions Practice Problems
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
- NMR spectroscopy – An Easy Introduction
- NMR Chemical Shift
- NMR Chemical Shift Range and Value Table
- NMR Number of Signals and Equivalent Protons
- Homotopic Enantiotopic Diastereotopic and Heterotopic
- Homotopic Enantiotopic Diastereotopic Practice Problems
- Integration in NMR Spectroscopy
- Splitting and Multiplicity (N+1 rule) in NMR Spectroscopy
- NMR Signal Splitting N+1 Rule Multiplicity Practice Problems
- 13C Carbon NMR
- DEPT NMR: Signals and Problem Solving
- NMR Spectroscopy-Carbon-Dept-IR Practice Problems
Organic Structure Determination
- NMR Spectroscopy-Carbon-Dept-IR Practice Problems
- Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy with Lots of Real Spectrum Practice Problems
Radical Reactions
- Free-Radical Addition of HBr: Anti-Markovnikov Addition
- Initiation Propagation Termination in Radical Reactions
- Selectivity in Radical Halogenation
- Stability of Radicals
- Resonance Structures of Radicals
- Stereochemistry of Radical Halogenation with Practice Problems
- Allylic Bromination by NBS with Practice Problems
- Radical Halogenation in Organic Synthesis
Reactions of Alcohols
- Nomenclature of Alcohols: Naming Alcohols based on IUPAC Rules with Practice Problems
- Preparation of Alcohols via Substitution or Addition Reactions
- Reaction of Alcohols with HCl, HBr and HI Acids
- Mesylates and Tosylates as Good Leaving Groups
- SOCl2 and PBr3 for Conversion of Alcohols to Alkyl Halides
- The Williamson Ether Synthesis
- POCl3 for Dehydration of AlcoholsAlcohols in Substitution Reactions with Tons of Practice Problems
- Dehydration of Alcohols by E1 and E2 Elimination
- LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism
- Alcohols from Carbonyl Reductions – Practice Problems
- Grignard Reaction in Preparing Alcohols with Practice Problems
- Grignard Reaction in Organic Synthesis with Practice Problems
- Protecting Groups For Alcohols and Their Use in Organic Synthesis
- Oxidation of Alcohols: PCC, PDC, CrO3, DMP, Swern and All of That
- NaIO4 Oxidative Cleavage of Diols
Epoxides
- Preparation of Epoxides
- Reactions of Epoxides Practice Problems
Conjugated Systems
- Resonance and Conjugated Dienes
- Allylic Carbocations
- 1,2 and 1,4 Electrophilic Addition to Dienes
- Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Control of Electrophilic Addition to Dienes
The Diels-Alder Reaction
- Diels Alder Reaction: Dienes and Dienophiles
- Predict the Products of the Diels-Alder Reaction with Practice Problems
- Endo and Exo products of Diels-Alder Reaction with Practice Problems
- Regioselectivity of the Diels–Alder Reaction with Practice Problems
- Identify the Diene and Dienophile of the Diels–Alder Reaction with Practice Problems
- Diels Alder Reaction in Organic Synthesis Practice Problems
Aromatic Compounds
- Naming Aromatic Compounds
- Introduction to Aromatic Compounds
- Benzene – Aromatic Structure and Stability
- Aromaticity and Huckel's Rule
- Identify Aromatic, Antiaromatic, or Nonaromatic Compounds
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution – The Mechanism
- Friedel-Crafts Alkylation with Practice Problems
- Friedel-Crafts Acylation with Practice Problems
- The Alkylation of Benzene by Acylation-Reduction
- Ortho Para Meta Directors in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution with Practice Problems
- Ortho Para and Meta in Disubstituted Benzenes
- Why Are Halogens Ortho-, Para- Directors yet Deactivators ?
- Limitations on Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
- Orientation in Benzene Rings With More Than One Substituent
- Synthesis of Aromatic Compounds From Benzene
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution with Arenediazonium Salts
- Reactions at the Benzylic Position
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones
- How to Name a Compound with Multiple Functional Groups
- Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups
- The Addition-Elimination Mechanism
- Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds by Hydride Ion
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Water
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Alcohols: Acetals and Hemiacetals
- Acetals as Protecting Groups for Aldehydes and Ketones
- Imines from Aldehydes and Ketones with Primary Amines
- Enamines from Aldehydes and Ketones with Secondary Amines
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Amines-Practice Problems
- Acetal Hydrolysis Mechanism
- Imine and Enamine Hydrolysis Mechanism
- The reaction of Aldehydes and Ketones with CN Cyanohydrin Formation
- Hydrolysis of Acetals, Imines and Enamines-Practice Problems
- The Wittig Reaction: Examples and Mechanism
- The Wittig Reaction-Practice Problems
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives-Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
- Fischer Esterification
- Ester Hydrolysis by Acid and Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
- What is Transesterification?
- Esters Reaction with Amines – The Aminolysis Mechanism
- Ester Reactions Summary and Practice Problems
- Preparation of Acyl (Acid) Chlorides (ROCl)
- Reactions of Acid Chlorides (ROCl) with Nucleophiles
- Reaction of Acyl Chlorides with Grignard and Gilman (Organocuprate) Reagents
- Reduction of Acyl Chlorides by LiAlH4, NaBH4, and LiAl(OtBu)3H
- Preparation and Reaction Mechanism of Carboxylic Anhydrides
- Amides – Structure and Reactivity
- Amides Hydrolysis: Acid and Base-Catalyzed Mechanism
- Amide Dehydration Mechanism by SOCl2, POCl3, and P2O5
- Amide Reduction Mechanism by LiAlH4
- Amides Preparation and Reactions Summary
- Amides from Carboxylic Acids-DCC and EDC Coupling
- The Mechanism of Nitrile Hydrolysis To Carboxylic Acid
- Nitrile Reduction Mechanism with LiAlH4 and DIBAL to Amine or Aldehyde
- The Mechanism of Grignard and Organolithium Reactions with Nitriles
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Practice Problems
Alpha Carbon Chemistry: Enols and Enolates
- Alpha Halogenation of Enols and Enolates
- The Haloform and Iodoform Reactions
- Alpha Halogenation of Carboxylic Acids
- Alpha Halogenation of Enols and Enolates Practice Problems
- Aldol Reaction – Principles and Mechanism
- Aldol Condensation – Dehydration of Aldol Addition Product
- Intramolecular Aldol Reactions
- Aldol Addition and Condensation Reactions – Practice Problems
- Crossed Aldol And Directed Aldol Reactions
- Crossed Aldol Condensation Practice Problems
- Alkylation of Enolates Alpha Position
- Enolate Alkylation Practice Problems
- Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis
- Acetoacetic Ester Enolates Practice Problems
- Malonic Ester Synthesis
- Michael Reaction: The Conjugate Addition of Enolates
- Robinson Annulation, Shortcut, and Retrosynthesis
- Claisen Condensation
- Dieckmann condensation – An Intramolecular Claisen Reaction
- Crossed Claisen and Claisen Variation Reactions
- Claisen Condensation Practice Problems
- Stork Enamine Synthesis
- Enolates in Organic Synthesis – a Comprehensive Practice Problem
Amines
- Preparation of Amines
- The Gabriel Synthesis of Primary Amines
- The Hofmann Elimination of Amines and Alkyl Fluorides
- Imines from Aldehydes and Ketones with Primary Amines
- Enamines from Aldehydes and Ketones with Secondary Amines
- The Reaction of Amines with Nitrous Acid
- Reactions of Amines Practice Problems
Organic Synthesis Problems
- Organic Chemistry Multistep Synthesis Practice Problems
- Acetals as Protecting Groups for Aldehydes and Ketones
- How to Choose Molecules for Doing SN2 and SN1 Synthesis-Practice Problems
- Alkene Reactions Practice Problems
- Changing the Position of a Double Bond
- Changing the Position of a Leaving Group
- Alkenes Multi-Step Synthesis Practice Problems
- Alkyne Synthesis Reactions Practice Problems
- Radical Halogenation in Organic Synthesis
- Grignard Reaction in Organic Synthesis with Practice Problems
- Ortho Para Meta Directors in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution with Practice Problems
- Orientation in Benzene Rings With More Than One Substituent
All the practice problems areopen to everyone for free! I have seen and prepared hundreds of exams for organic chemistry and these practice problems are the types thatyou will find in your exams. Their difficulty varies from one-step to more advanced ones including step organic synthesis problems.
After working on each question, you have the possibility to first check your answerand then refer to thestep-by-step solution .
The practice problems are the only ones you get to do.
Multiple choice quizzes might be the "easy" way of glancing through the key concepts and getting feedback on what you need to work more.
These are also included in your Chemistry Steps membership.
Molecular Representations
Energy Changes In Organic Chemistry
Source: https://www.chemistrysteps.com/organic-chemistry-practice-problems/
0 Response to "Chemistry 1 Formula Writting and Naming Continued Practice Extra Practice for Quiz 1"
Post a Comment